Create a Batch registration Function Using Upload¶
This section describes the function to upload a CSV file for batch registration based on an example application.
- Description of the function to be created
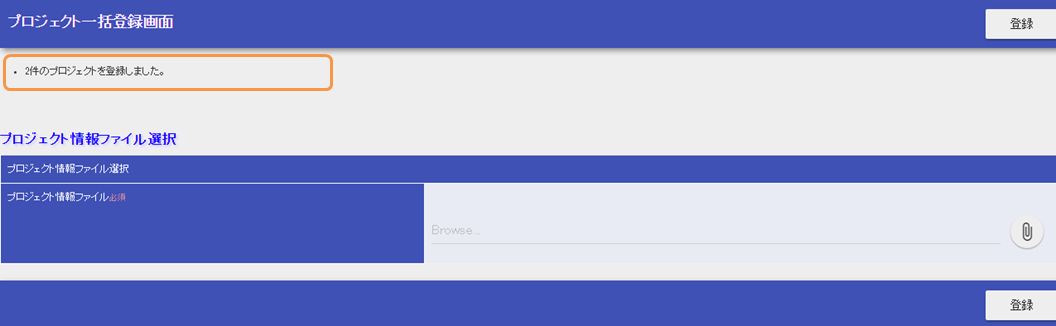
- Click “Project batch registration (プロジェクト一括登録)” in the header menu.
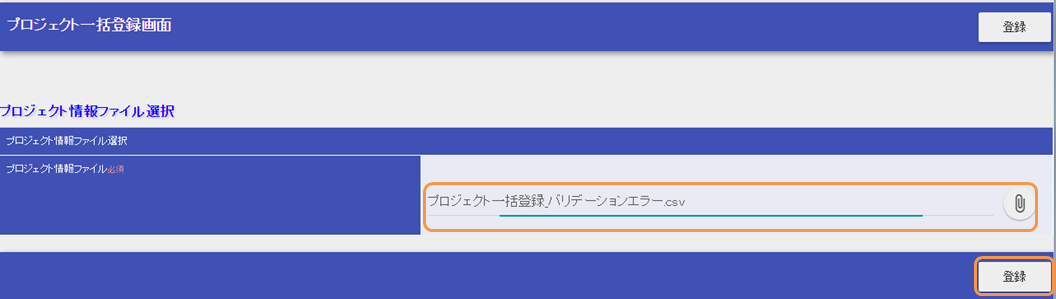
Download the batch registration sample file which generates the validation error from below
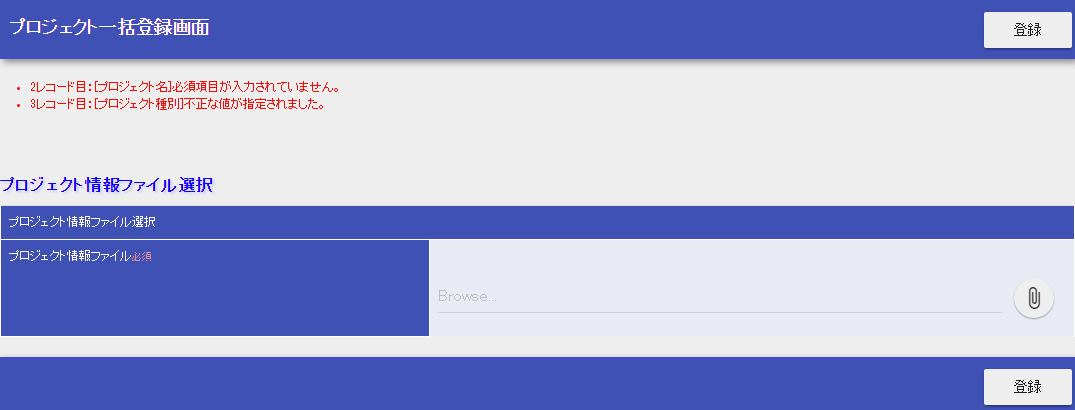
batch_project_registration_validation_error.csv(プロジェクト一括登録_バリデーションエラー.csv)Upload the sample file and click the “Register(登録)” button.
- Validation error occurs.
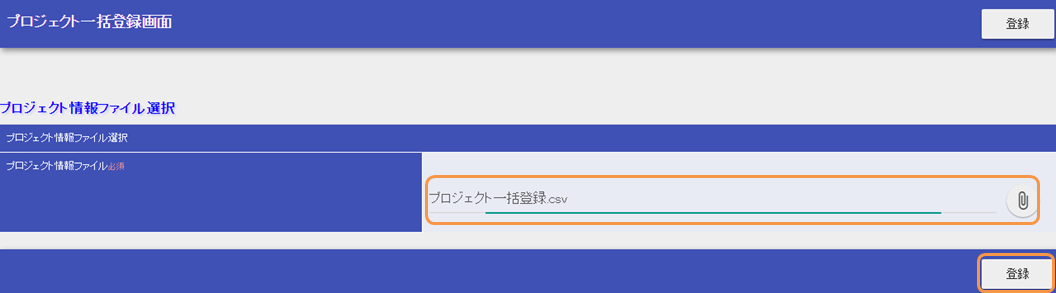
- Download the batch registration sample file which does not generate validation error from below
project_batch_registration.csv(プロジェクト一括登録.csv)- Upload the sample file and click the “Register(登録)” button.
- The contents of the file are registered in the database and the completion message is displayed.
Overview of the business action method to be created¶
- ProjectUploadAction.java
The processing flow of the business action method is as follows.
- Acquire a file
- Validate the contents of the CSV file by binding to Bean
- Batch registration to DB
- Saving a file
The details of each process is described under Implementation of the file upload function and Implementation of the batch registration function.
Implementation of the file upload function¶
First, how to create the upload part of the batch registration function using upload is explained
- Create a file upload screen
Create a screen with a file upload field.
- /src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/view/projectUpload/create.jsp
- Key points of this implementation
- Specify multipart/form-data as enctype attribute of form tag to send multipart file.
- Create a file upload field using file tag. Specify the registration name of the request object in the name attribute. To acquire the file in a business action, specify this registration name as an argument of HttpRequest#getPart
- Display upload completed message with message tag, once the upload is completed. In order to include the number of uploads in the completion message, specify the number of uploads configured in the request scope in option0 attribute.
- Use errors tag to create an area to display the list of validation error messages for the target file. For the output format of the error message list, refer to error message list.
- Create a business action method
Describes how to get and save a file in the business action method.
- ProjectUploadAction.java
- Key points of this implementation
Acquire the file HttpRequest#getPart.
When the file does not exist (not uploaded), then the size of PartInfo list that is acquired will be zero. This value is used to perform control such as throwing a business exception.
The uploaded file is stored in a temporary area by the multipart request handler. Since the temporary area is automatically deleted, if you need to permanently (save) an uploaded file, move the file to an arbitrary directory. However, file transfers are possible only when the file path management is used to manage the input and output of files and directories.
Use UploadHelper#moveFileTo method to transfer files. The first argument is the key name of the file storage directory registered in the configuration file. In the Example Application, the configuration is described in the following file.
- filepath-for-webui.xml
Implementation of the batch registration function¶
This section describes how to create the batch registration part of the batch registration function using uploads.
- Create a bean to bind the contents of the file
A bean to bind the contents of the file is created.
- ProjectUploadDto.java
@Csv(headers = { /** Describe the header **/}, properties = { /** Properties to bind **/}, type = Csv.CsvType.CUSTOM) @CsvFormat(charset = "Shift_JIS", fieldSeparator = ',',ignoreEmptyLine = true, lineSeparator = "\r\n", quote = '"', quoteMode = CsvDataBindConfig.QuoteMode.NORMAL, requiredHeader = true, emptyToNull = true) public class ProjectUploadDto implements Serializable { // Excerpt of some items only.Getter and setter are omitted /** Project name */ @Required(message = "{nablarch.core.validation.ee.Required.upload}") @Domain("projectName") private String projectName; /** Project type */ @Required(message = "{nablarch.core.validation.ee.Required.upload}") @Domain("projectType") private String projectType; // Property that holds the line count to process.Setter is omitted. /** Line count*/ private Long lineNumber; /** * Get line count. * @return Line count */ @LineNumber public Long getLineNumber() { return lineNumber; } }
- Key points of this implementation
- Use @Csv for configuration to link the contents of the uploaded CSV file with the bean property. Use @CsvFormat to specify the acceptable CSV format. ( @CsvFormat is not required when using the default format specification) For information on how to configure the annotation, refer to format specification method when binding the CSV file to the Java Beans class.
- Perform Bean Validation by assigning annotations for validation of @Required and @Domain to the property.
- To accept the values from a file, property is defined as string type, and conversion to an appropriate type is performed as per the safe value that has passed the validation.
- By defining the line count property and granting LineNumber to the getter, the line of the target data can be configured automatically.
Tip
The validation error message of a required input item is changed to an appropriate value as per the file upload. For information on how to specify a validation message, refer to configure the input value check rule.
- Create a business action method
Create a business action method to register the contents of the uploaded file in the database.
- Validate the contents of 1 CSV file by binding to Bean
- ProjectUploadAction.java
private List<Project> readFileAndValidate(final PartInfo partInfo, final LoginUserPrincipal userContext) { List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>(); List<Project> projects = new ArrayList<>(); // Validate the contents of the file by binding it to the bean try (final ObjectMapper<ProjectUploadDto> mapper = ObjectMapperFactory.create( ProjectUploadDto.class, partInfo.getInputStream())) { ProjectUploadDto projectUploadDto; while ((projectUploadDto = mapper.read()) != null) { // Validate and configure the result messages messages.addAll(validate(projectUploadDto)); // Create an entity projects.add(createProject(projectUploadDto, userContext.getUserId())); } } catch (InvalidDataFormatException e) { // Parsing ends if there is an invalid line in the file format messages.add( MessageUtil.createMessage( MessageLevel.ERROR, "errors.upload.format", e.getLineNumber())); } // Not registered in the database even if there is one error if (!messages.isEmpty()) { throw new ApplicationException(messages); } return projects; } /** * Validate the project information and store the result in the message list. * * @param projectUploadDto Project information Bean generated from CSV * @return messages List of validation result messages */ private List<Message> validate(final ProjectUploadDto projectUploadDto) { List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>(); // Single item validation.Execute Bean validation based on the annotation defined in Dto try { ValidatorUtil.validate(projectUploadDto); } catch (ApplicationException e) { messages.addAll(e.getMessages() .stream() .map(message -> MessageUtil.createMessage(MessageLevel.ERROR, "errors.upload.validate", projectUploadDto.getLineNumber(), message)) .collect(Collectors.toList())); } // Customer existence check if (!existsClient(projectUploadDto)) { messages.add(MessageUtil.createMessage(MessageLevel.ERROR, "errors.upload.client", projectUploadDto.getLineNumber())); } return messages; }
- Key points of this implementation
- Use ObjectMapper provided by DataBind to bind and get the file to the bean.
- By executing ObjectMapper#read for the acquired ObjectMapper object, the list of bound bean can be obtained.
- Validator object can be created by using ValidatorUtil#getValidator, and Bean Validation can be executed for any Bean.
- When verification is continued up to the last row and not aborted even when an error occurs, error messages for all rows are stored after the verification is completed in Message list, by generating and throwing ApplicationException with this list as an argument, it can be output to the screen with errors tag.
- For how to assign a property name to the validation message, implement by referring to how to include item names in the message when a validation error occurs.
- 2.Batch registration to DB
- ProjectUploadAction.java
public HttpResponse upload(HttpRequest request,ExecutionContext context) throws IOException { // Execution of validation is described above // Batch registration to DB insertProjects(projects); // Saving a file is described above } /** * Register multiple project entities to the database in a batch. * @param projects List of validated projects */ private void insertProjects(List<Project> projects) { List<Project> insertProjects = new ArrayList<Project>(); for (Project project : projects) { insertProjects.add(project); // Batch insert every 100 records if (insertProjects.size() >= 100) { UniversalDao.batchInsert(insertProjects); insertProjects.clear(); } } if (!insertProjects.isEmpty()) { UniversalDao.batchInsert(insertProjects); } }
- Key points of this implementation
- Batch registration is executed using UniversalDao#batchInsert.
- Set an upper limit on the number of registrations per batch registration, because a large number of registrations at a time may result in a deterioration in performance.
This completes the explanation for the batch registration function using upload.