Responsibility Assignment of the Application¶
This section describes the classes to be implemented when creating web applications and their responsibilities.
Classes and their responsibilities
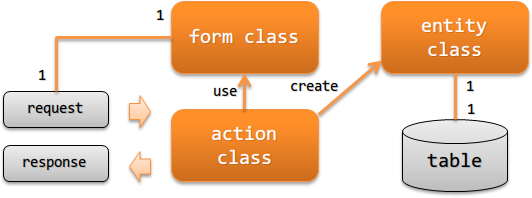
- Action class
The action class executes the business logic based on the request and generates and returns the response.
For example, create an entity class from a form class and persist its contents to a database.
- Form class
Class to map the input value (http request) from the screen.
Has the annotation configuration for validation of the request and logic for correlation validation. Depending on the request from the outside, it may have a hierarchical structure (form having a form).
- Form class is created for each HTML form
The form class defines the interface with the screen, and a separate form class is created if the interface (HTML form) is different. For example, the interface (HTML form) is different even in the case of registration and update screens that often have similar input items, and a different form class is required.
By creating a form class for each interface (HTML form), the request parameters accepted by the server to those defined in the HTML form can be limited. As a result, even if an unexpected parameter (invalid parameter) is submitted by the client, the parameter is excluded when it is converted to a form class, and security can be improved. Since the form class only has validation logic for one interface, its responsibilities are clear and is more readable and maintainable.
The logic of correlation validation may be the same for multiple form classes. In this case, it is better to extract the logic of correlation validation into a separate class and make the logic common.
- All the form class properties must be defined by a String
- See Bean Validation for the reason why the property must be a String.
- Form class object is not saved in the session
- See session store for reasons why the object should not be stored in a session.
- Entity class
- A class with a one-to-one correspondence with a table. Has the property corresponding to columns.